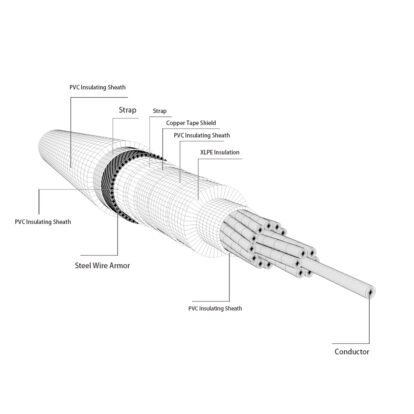
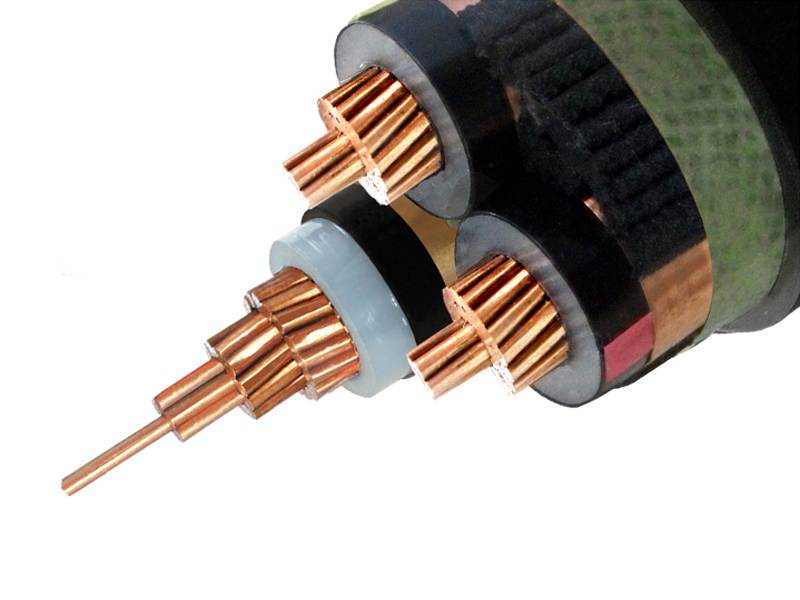
In the power distribution system, the medium-voltage power cables, which are the main lines for transmitting electric energy, often cause failures due to various hidden problems in the construction process.

Low-voltage power cables have low voltage, simple structure, and simple construction and installation. As long as a little attention is paid when laying, the hidden danger of failure can be greatly reduced. However, due to the concealment, complex structure, high voltage, and cumbersome construction and installation of medium-voltage power cables, once the professional quality and skills of the construction personnel are slightly lacking, the laying, installation, and grounding of medium-voltage power cables in accordance with the drawings and normalized operation cannot be achieved,it will bury hidden troubles for the safe operation of the power distribution system, and the causes of failures are complex and diverse. At present, line faults caused by poor installation quality of cable accessories have accounted for more than 80% of all medium-voltage power cable line faults.In order to ensure the safe operation of the medium-voltage power cable distribution system, this paper points out in detail the matters that should be paid attention to when laying, installing and grounding medium-voltage power cables during construction.
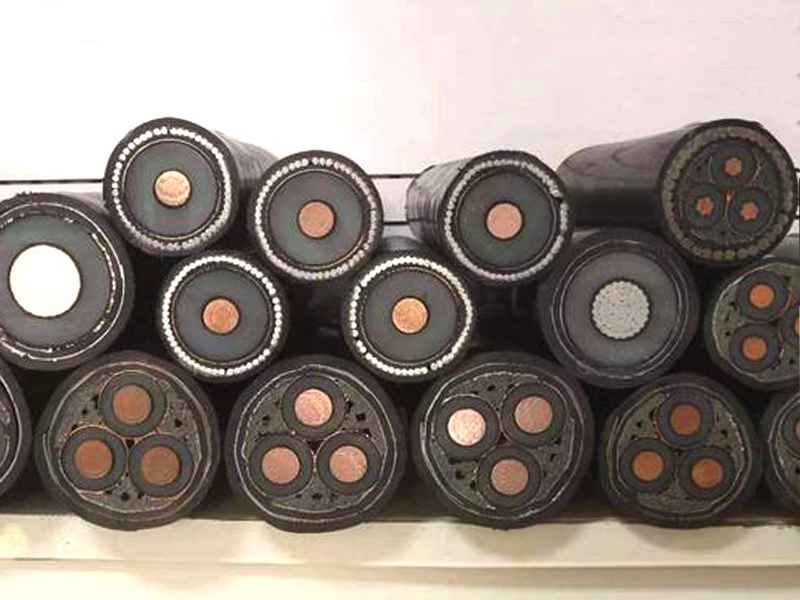
Laying of medium voltage cables

When choosing the laying path of medium-voltage power cables, it is necessary to avoid sections where the cables are likely to suffer from external forces, overcooling, overheating, corrosion, demolition, etc.Large drops in cable lines should be avoided.Except for waterproof cables, cables should avoid long-term In the water.It should be ensured that the cable laying channel is unimpeded, all sundries have been removed, and the drainage is good. The structures passing through have been constructed, and the turning radius of the cable trench and the turning of the civil part of the tunnel is not less than the minimum allowable bending radius for laying cables.
Pay attention to the following aspects when laying medium voltage power cables:
- The ambient temperature at the laying site should generally not be lower than 0°C. If the construction period is urgent in winter (the ambient temperature at the laying site is lower than 0°C), the cable can be preheated by powering on or placed in a drying room.When the surface temperature reaches 20-30°C,the laying can be carried out quickly . When the cable has cooled below 0 °C, it shall not be bent again.
- Measures should be taken to prevent the cable from being grazed by the ground, trench wall, pipe mouth, and machinery. Once the cable grazes are found, the laying must be stopped immediately. Only when the cause of the grazes is found out and removed, can the laying be carried out again.
- Twisting is not allowed, so as not to damage the cable. In order to eliminate the twisting stress of the cable, an anti-twisting device should be installed at the cable pulling head. For coiled cables and short cables that are not coiled, they should be turned in the direction of the circle when laying to prevent the cables from twisting. If twisting has been caused, it should be released along the twisting direction. Do not hit the cable with any tools or objects to prevent cables from damaging.
- Use special equipment and tools that meet the requirements (such as pay-off racks and guide wheels) for laying, and choose laying methods such as end traction laying, mechanical conveying laying, and manual-assisted guiding synchronous laying according to site construction conditions.
- The maximum lateral pressure, maximum traction force, and minimum allowable bending radius of the cable during and after laying should not exceed the specified value allowed by the cable.
- When there are many cables laid in trenches, pipes and tunnels, attention should be paid to ventilation and heat dissipation.When the medium voltage power cable is directly buried, the buried depth of the cable (the distance between the upper surface of the cable and the ground) should not be less than 700mm.The bottom of the ditch must have a good soil layer, free of hard debris, and be paved with 100mm thick fine soil or yellow sand. After the cable is laid, it should be covered with 100mm thick fine soil or yellow sand, and then covered with concrete or bricks, etc. The covering width of the protective cover should exceed 50mm on both sides of the cable, and measures should be taken to prevent the migration of soil moisture.After re-soiling, path signs should be installed on the ground. In cold regions, cables should be laid below the permafrost layer, and if the ground conditions are not suitable for deep burial, protective measures should be taken to avoid damaging cables.The clear distance between direct buried cables and various facilities in parallel or across them shall comply with relevant regulations.
In addition, in order to ensure the safety of medium-voltage power cables during operation, the following aspects should also be paid attention to during laying.The rated voltage of the cable laying should not be less than the working voltage of the system, and the maximum voltage of the system should not exceed 1.2 times the rated voltage of the cable.The long-term maximum working temperature of the laying cable should not exceed 90 ℃.At 5S short-circuit current, the maximum temperature of the conductor should not exceed Exceeding 250 ℃. It is strictly forbidden to overload the cable for a long time.
Installation of medium voltage cables

The installation of medium-voltage power cable terminal accessories and intermediate joints is the weakest link in the construction process of medium-voltage power cables, and the installation quality will directly affect the safe operation of the entire power distribution system.According to incomplete statistics, line faults caused by poor installation quality account for more than 80% of all line faults. In this regard, sufficient attention should be paid during the construction of medium-voltage power cables to ensure high-quality completion of the installation of medium-voltage power cables.
Medium-voltage power cable terminal accessories can generally be divided into two types: cold-shrinkable cable accessories and heat-shrinkable cable accessories. According to the characteristics of cable materials, user requirements and current construction conditions, it is recommended to choose cold shrinkable cable accessories. Although the price is higher, the safety is also higher.The installation process of medium-voltage power cable terminal accessories is as follows: strip the outer sheath of the cable → remove the steel tape armor layer (optional, if there is, check whether the armor material of the single-core cable is a non-magnetic metal tape) → strip the cable Isolation sleeve → Weld copper tape shielding grounding wire (make the wire core marking line) → Strip the insulation shielding layer (10KV cable insulation semi-conductive shielding layer is generally peelable and easy to peel off; 35KV cable insulation semi-conductive shielding layer is not Peel-off type, special care should be taken not to damage the insulation layer when handling) → clean the insulating surface → install semi-conductive tubes → install branch gloves → strip off the insulation layer and conductor shielding layer → install insulating sleeves and terminals. Pay attention to the following aspects during the installation of medium voltage power cable terminal accessories:
- The copper strip ground wire should be welded firmly.
- Do not damage the conductor when stripping the shielding layer of the conductor, which will cause burrs on the conductor and cause the partial discharge of the cable to exceed the standard.
- The wiring terminal should match the cable conductor material. The aluminum core conductor should use a high-quality copper-aluminum transition terminal, and the terminal should be filled with conductive paste. When crimping, start from the end of the terminal and crimp it in place.
- The contact surface between the cable insulation and the terminal should be processed perfectly to ensure a good seal, otherwise it will cause many fault points.
The installation process of the intermediate joint of the medium-voltage power cable is basically the same as that of the terminal accessories, with some differences. The following aspects should be paid attention to in the specific operation:
- Accurately measure the length of the two connecting cables at the joint to avoid the two connecting cables being out of reach.
- Strictly control the stripped length of each layer at the end of the two connecting cables, and strive to be consistent.
- When crimping the straight-through terminal, the straight-through tube should be crimped with the three wire cores of one connecting cable first, and then crimped with the three wire cores of the other connecting cable.
- The copper strip ground wire should be firm, and the wire core mark should be clear.
- At the joint, the two ends of the copper wire shielding braid of the three cores should be in full contact with the copper tapes of the two joint cables.
Grounding of medium voltage cables
In the past, in the faults of medium-voltage power cables, there were often cases of short-circuit caused by severe heating of a certain phase of the cable. After dissecting the faulty cable, it was found that the insulation core of the cable was intact, and the copper tape had burns that were not penetrated, but the rest of the cable had been burnt and charred, and all signs indicated that it was burned from the outside to the inside, which indicated that there was no problem with the cable conductor itself during operation. It is other reasons that cause the cable to heat up and carbonize. It is confirmed by analysis that when the medium-voltage power cable is running under alternating voltage, the alternating current passing through the conductor will generate an alternating magnetic field, and the magnetic field lines generated by the magnetic field are connected to the conductor, and are also connected to the metal sheath (shielding layer and armoring layer) ), so that an induced voltage is generated in the metal sheath. If the induced voltage is too high, and the medium voltage power cable is not safely grounded during the actual construction process of the medium voltage power cable, a large induced current will be generated in the metal sheath , causing the cable to heat up severely, resulting in a short circuit fault. Therefore, in order to ensure the stable, reliable and safe operation of the system, it is necessary to adopt a correct and safe grounding method according to the induced voltage and circulating current generated in the metal sheath of the medium-voltage power cable, so as to reduce the risk of system line heating and short-circuit failure.
Conclusion:
Considering that the construction process of medium voltage power cables has the characteristics of high voltage, multiple shielding, long lines, harsh site environment, and high construction requirements, this paper introduces in detail the matters that should be paid attention to during laying, installation, and grounding during construction. However, there are many situations in the laying, installation, and grounding methods of medium-voltage power cables, and the buried laying and cable trench laying methods with high concealment are mostly used, resulting in complex and diverse cable faults, which increase the analysis, location, and location of cable fault points. It is difficult to find and repair. Therefore, the professionalism and basic skills of cable construction personnel and management personnel are very important for high-quality completion of cable laying, installation, and grounding. During construction and management, it is necessary to standardize operations and construct according to drawings. Technical points in the laying process to avoid failures.