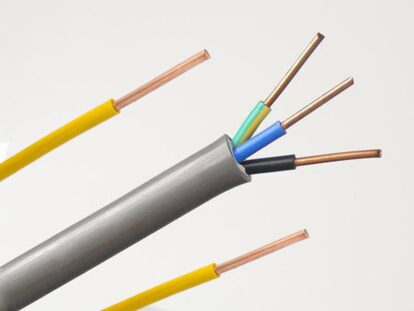
The 0.6 / 1KV overhead insulated cable is an overhead wire equipped with an insulating layer. AAC, AAAC, ACSR strands are generally selected for conductor. The insulation material is 90℃ XLPE.
This Peruvian technical standard specifies the requirements that must be met by copper or aluminum conductors, insulated with cross-linked polyethylene (xlpe), placed in a spiral on a supporting cable.
Features
1.Low operating cost
Compared with underground cables, the construction, operation and maintenance costs of overhead insulated cables are lower, because they are easier to repair and replace, and do not require underground laying, excavation, backfilling, etc.
2.Easy troubleshooting
The fault location of underground cables is more troublesome, and the repair time will be longer, while the fault of overhead insulated cables is easy to find and locate, and can be repaired faster to ensure the reliability of power supply.
3.Wide range of application
Aerial insulated cables have stronger environmental adaptability and can be used in various harsh environments, such as strong winds and lightning strikes, while underground cables are greatly affected by geological conditions and the environment, and may not be suitable for all regions and application scenarios.
4.Fast construction speed
The construction speed of overhead insulated cables is faster, because it is not restricted by terrain and buildings, the construction speed is faster, and it can be directly erected in the air.
Application
Aerial insulated cables are often used in urban and rural power grid reconstruction, road lighting and other lines.
1.Power transmission
Overhead insulated wires can transport the power generated by the power plant to substations in various cities and regions
2.Power distribution
Aerial insulated cables convert high-voltage power from substations into low-voltage power and deliver it to homes, commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and other places for people to consume.
3.Power supply to electric railways
Overhead insulated wires can provide power for electrified railways such as trams and subways.
Construction
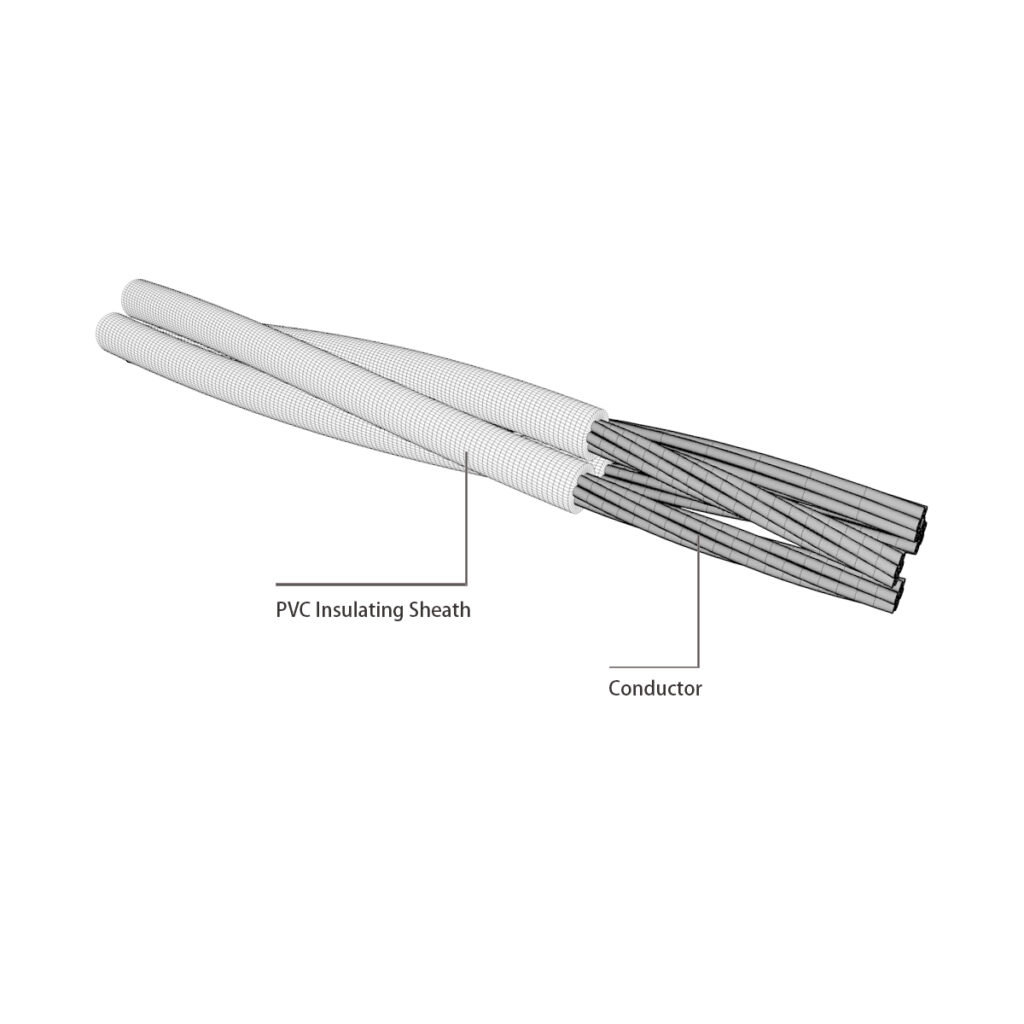
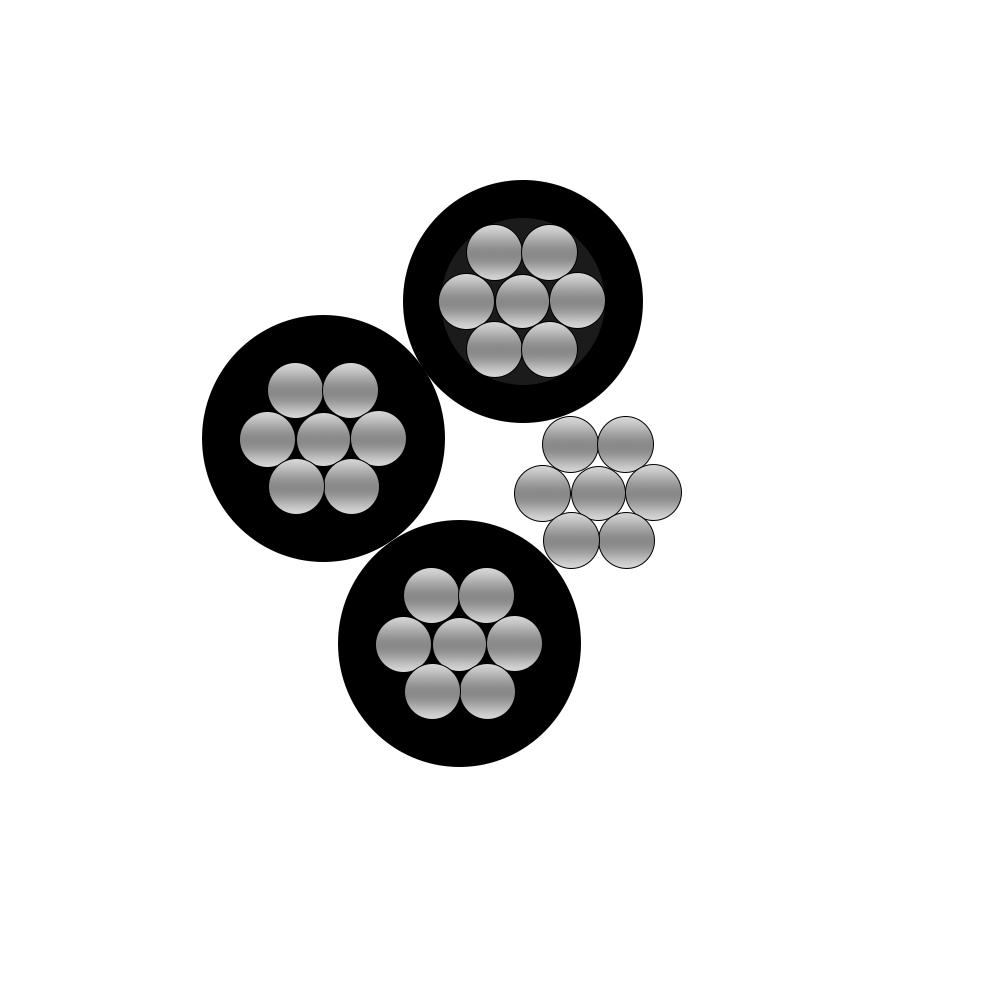
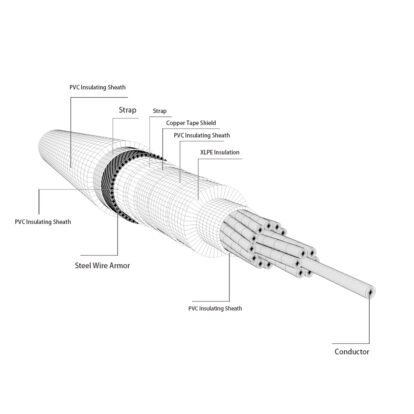
1.Conductor
The core of the conductor is a circular cross-section, the outermost layer of the conductor is stranded on the left, and the conductor material used is steel-cored aluminum stranded wire or aluminum alloy stranded wire
2.insulation
The insulation layer of ABC cables is usually made of cross-linked polyethylene material, which has excellent pressure resistance and insulation properties. The thickness of the insulating layer can be designed and adjusted according to the use environment and electrical requirements.
3.Cabling
Multi-core cables (multiple-conductors) should be cabled, the cabled direction is right, and the cabled pitch ratio is 60 times.
Performance
| Section nominal | Nominal insulation thickness | Maximum wiring passage | spark voltage Alternating current | spark voltage DC |
| mm2 | mm | mm | KV | KV |
| 10 16 25 35 50 70 95 120 150 185 240 | 1.14 1.14 1.14 1.14 1.52 1.52 1.52 2.03 2.03 2.03 2.03 | 389 453 530 601 742 843 950 1109 1210 1315 1464 | 10.0 10.0 12.5 15.0 15.0 15.0 15.0 15.0 15.0 15.0 17.5 | 16.5 16.5 21.0 24.0 24.0 24.0 24.0 24.0 24.0 24.0 30.0 |