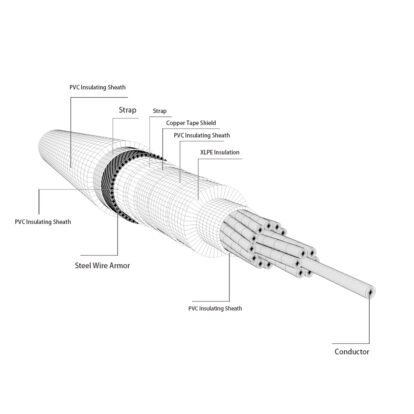
In order to protect the structural integrity and electrical performance of the cable and improve the service life of the cable, it is very necessary to add an armor layer to the outer sheath of the cable. The armor of the cable usually has two types: steel belt armor and steel wire armor.
In order to enable the cable to withstand radial pressure, a double-layer steel belt and gap winding process are used, which is called steel belt armored cable; after cabling, the steel belt is wound around the cable core and then extruded into a sheath. The representation methods of this type of cable model include control cable KVV22, plastic cable VV22, communication cable SYV22, etc.
The two Arabic numerals in the subscript of the cable model, the first one: "2" represents double steel belt armor; the second one: "2" represents polyvinyl chloride sheath, such as "2" with polyethylene sheath "changed to" 3. This type of cable is generally used in places where it is subjected to relatively large pressure. For example: crossing the road, square, road and railway with large vibration, etc., suitable for burial, tunnel and pipeline laying.
In order to enable the cable to withstand large axial tension, multiple low-carbon steel wires are wound together, which is called steel wire armored cable. After the cable is formed, the steel wire is wound around the core wire according to the necessary pitch, and then the sheath is extruded. The representation methods in the cable model are such as control cable KVV32, plastic cable VV32, coaxial cable HOL33, etc. The two Arabic numerals in the model, the first one: "3" represents fine steel wire armor; the second one: "2" represents PVC sheath, and "3" represents polyethylene sheath. This type of cable is generally used in occasions with large spans and large laying drops.
The role of armored cable
Armored cable refers to a cable with a metal armored protective layer. The purpose of adding an armor layer to the cable is not only to enhance mechanical protection such as tensile and compressive resistance to extend the service life, but also to improve the anti-interference performance of the cable through shielding protection. .
Commonly used armor materials include steel belt, steel wire, aluminum belt, aluminum tube, etc. Among them, the steel belt and steel wire armor layer have high magnetic permeability and good magnetic shielding effect. They can be used to resist low-frequency interference and enable armored cables to be laid directly without passing through pipelines. They are widely used in practice and are inexpensive and good quality.
The armored cable mechanical protection layer can be added to cables of any structure to increase the mechanical strength of the cable and improve its corrosion resistance. It is a special cable designed for areas susceptible to mechanical damage and corrosion. It can be laid in any way and is more suitable for direct burial in rocky areas. Generally speaking, armored cables are buried wires and cables. The purpose of adding armor to power line transmission power cables is to enhance mechanical protection such as tensile and compressive resistance and extend service life. The resistance to external forces can also put some rats biting to avoid power transmission problems through the armor. The bending radius of the armor should be large, and the armor layer can be grounded to protect the cable.